How do you calculate acceleration from a distance time graph?
How do you calculate acceleration from a distance time graph?

Is there acceleration in distance time graph?
If the speed of an object changes, it will be accelerating or decelerating . This can be shown as a curved line on a distance-time graph. If an object is accelerating or decelerating, its speed can be calculated at any particular time by: drawing a tangent to the curve at that time.
How do you find acceleration from a graph?
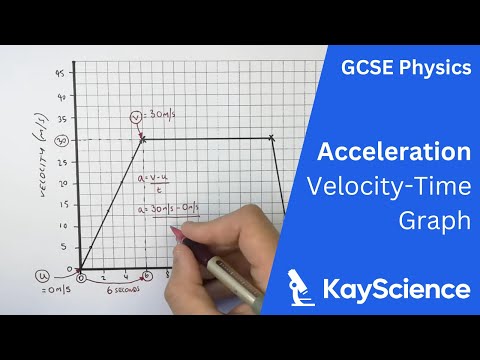
What is the formula for acceleration with distance?
We can derive an equation linking the acceleration and the distance as follows. We can rewrite the average velocity, 𝑣 a v , as 𝑣 = 𝑣 + 𝑢 2 , a v where 𝑣 is the final velocity and 𝑢 is the initial velocity. We can use our definition of acceleration as 𝑎 = Δ 𝑣 Δ 𝑡 to rewrite Δ 𝑡 as Δ 𝑡 = Δ 𝑣 𝑎 = 𝑣 − 𝑢 𝑎 .
What are the 4 equations for acceleration?
Equations of Motion
| Variable | Equation |
|---|---|
| Velocity | v, equals, u, plus, a, t,v=u+at |
| Displacement with positive acceleration | s, equals, u, t, plus, one half, a, t, squared,s=ut+21at2 |
| Displacement knowing initial and final velocities | s, equals, one half, left bracket, u, plus, v, right bracket, t,s=21(u+v)t |
What is acceleration on a time graph?
The area under an acceleration graph represents the change in velocity. In other words, the area under the acceleration graph for a certain time interval is equal to the change in velocity during that time interval.
Is acceleration the slope of a distance time graph?
It was learned earlier in Lesson 4 that the slope of the line on a velocity versus time graph is equal to the acceleration of the object. If the object is moving with an acceleration of +4 m/s/s (i.e., changing its velocity by 4 m/s per second), then the slope of the line will be +4 m/s/s.
Does the slope of distance time graph gives acceleration?
On a distance-time graph, a sloping line indicates that the object is moving. The slope or gradient of the line in a distance-time graph equals the speed of the object. The faster the object moves, the steeper the line (and the greater the gradient).
How do you find velocity from a distance time graph?
How do you calculate acceleration from slope?
If a particle of mass m is placed on a smooth inclined plane (i.e. the frictional force F=0 ) and released it will slide down the slope. To find the acceleration of the particle as it slides we resolve in the direction of motion. F=ma,mg cos(90∘−θ)=ma,g cos(90∘−θ)=a,g sin(θ)=a.
How do you find acceleration using slope?
a = 2 d t 2 . This equation tells us that, for constant acceleration, the slope of a plot of 2d versus t2 is acceleration, as shown in Figure 3.8. Figure 3.8 When acceleration is constant, the slope of 2d versus t2 gives the acceleration. v 2 = v 0 2 + 2 a ( d − d 0 ) .
Which slope of graph gives acceleration?
(b) The acceleration is defined as the rate of change of speed. So, the slope of the Speed (a velocity) arid Time graph gives acceleration.
What are the 3 formulas for acceleration?
Acceleration formula – three acceleration equations
- a = (v_f – v_i) / Δt ;
- a = 2 × (Δd – v_i × Δt) / Δt² ;
- a = F / m ;
What are the 2 formulas for acceleration?
To calculate acceleration, use the equation a = Δv / Δt, where Δv is the change in velocity, and Δt is how long it took for that change to occur. To calculate Δv, use the equation Δv = vf – vi, where vf is final velocity and vi is initial velocity.
How do you find acceleration with distance and change?
How do you calculate the acceleration?
Acceleration (a) is the change in velocity (Δv) over the change in time (Δt), represented by the equation a = Δv/Δt. This allows you to measure how fast velocity changes in meters per second squared (m/s^2).
