How do you calculate variable acceleration?
How do you calculate variable acceleration?
v = d x d t = ( 5 t 4 − 24 t ) m s − 1 . This is the equation for the velocity of the particle. Differentiating again gives us the formula for the acceleration of the particle a=d2xdt2=(20t3−24)ms−2.
What is an example of variable acceleration?
Variable acceleration- Motion of a vehicle on a crowded road.
What are the 3 formulas for acceleration?
Acceleration formula – three acceleration equations
- a = (v_f – v_i) / Δt ;
- a = 2 × (Δd – v_i × Δt) / Δt² ;
- a = F / m ;
How do you find distance traveled in a variable acceleration?
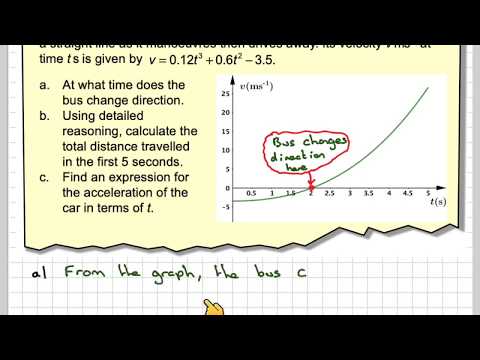
What is variable acceleration?
Variable acceleration. Here, equal changes in velocity occur in equal intervals of time. If change in velocity is not the same in the same intervals of time, then it is variable acceleration. Example- Motion of a body under gravity ( free fall of a body) Example- Motion of a vehicle on a hilly road.
What are the 4 equations for acceleration?
Equations of Motion
| Variable | Equation |
|---|---|
| Velocity | v, equals, u, plus, a, t,v=u+at |
| Displacement with positive acceleration | s, equals, u, t, plus, one half, a, t, squared,s=ut+21at2 |
| Displacement knowing initial and final velocities | s, equals, one half, left bracket, u, plus, v, right bracket, t,s=21(u+v)t |
What are the two variables of acceleration?
Newton’s second law states that the acceleration of an object depends upon two variables – the net force acting on the object and the mass of the object. The acceleration of the body is directly proportional to the net force acting on the body and inversely proportional to the mass of the body.
What are 4 examples of variables?
Height, age, income, province or country of birth, grades obtained at school and type of housing are all examples of variables.
What are 5 examples of acceleration?
Examples
- An object was moving north at 10 meters per second. …
- An apple is falling down. …
- Jane is walking east at 3 kilometers per hour. …
- Tom was walking east at 3 kilometers per hour. …
- Sally was walking east at 3 kilometers per hour. …
- Acceleration due to gravity.
How do you solve acceleration problems?
How do you find acceleration with velocity and distance without time?
If we have an initial velocity, a final velocity, and a distance but don’t know the time interval, we can apply the constant acceleration equation v2 = v02 + 2a𝛥x to get the acceleration. We can find acceleration with velocity and distance using the equation above.
What is the formula for acceleration with distance?
We can derive an equation linking the acceleration and the distance as follows. We can rewrite the average velocity, 𝑣 a v , as 𝑣 = 𝑣 + 𝑢 2 , a v where 𝑣 is the final velocity and 𝑢 is the initial velocity. We can use our definition of acceleration as 𝑎 = Δ 𝑣 Δ 𝑡 to rewrite Δ 𝑡 as Δ 𝑡 = Δ 𝑣 𝑎 = 𝑣 − 𝑢 𝑎 .
How do you find the distance formula with variables?
How do you calculate distance traveled when given velocity?
In the context of velocity and position, if we know a velocity function v, an antiderivative of v is a position function s that satisfies s 0 = v. If v is positive on a given interval, say [a, b], then the change in position, s(b) − s(a), measures the distance the moving object traveled on [a, b].
What is the unit of variable acceleration?
Acceleration can be defined as the rate of change of velocity with time. It can also be defined as the increase in velocity per second. The S.I. unit of acceleration is meter per second square or ms−2.
What is constant acceleration and variable acceleration?
In uniform or constant acceleration, the velocity of an object changes by an equal amount in every equal time period. If changes in velocity are not equal in the equal intervals of time, the acceleration is said to be variable.
What is the difference between constant acceleration and variable acceleration?
On a graph, it is represented on a velocity-time graph, and a straight line between them shows the uniform or constant acceleration. Non-uniform or variable acceleration is a type of motion in which the speed or velocity of an object changes by unequal amounts in equal interval of time.
How do you calculate a variable?
To calculate variable costs, multiply what it costs to make one unit of your product by the total number of products you’ve created. This formula looks like this: Total Variable Costs = Cost Per Unit x Total Number of Units.
What is variable formula?
In Maths, a variable is an alphabet or term that represents an unknown number or unknown value or unknown quantity. The variables are specially used in the case of algebraic expression or algebra. For example, x+9=4 is a linear equation where x is a variable, where 9 and 4 are constants.
What is the formula of variable velocity?
Determine the object’s original velocity by dividing the time it took for the object to travel a given distance by the total distance. In the equation V = d/t, V is the velocity, d is the distance, and t is the time.
What are the two formulas for acceleration?
The equation for calculating acceleration is:
- Acceleration = (change in velocity)/(change in time) or. a = Δv ÷ Δt.
- Force = mass * acceleration. or. F = ma.
- acceleration = force/mass. or. a = F/m.
