How do you find acceleration from velocity function?
How do you find acceleration from velocity function?

How do you find acceleration from a velocity graph in calculus?

What is the acceleration formula in calculus?
To find acceleration at time t, we have to differentiate the position vector twice. Differentiating the first time gives the velocity: v(t) = r'(t) = 12t3i + 12tj. Differentiating a second time gives the accelaration: a(t) = r”(t) = 36t2i + 12j.
How do you find acceleration from velocity integration?
The integral of acceleration over time is change in velocity (∆v = ∫a dt). The integral of velocity over time is change in position (∆s = ∫v dt).
What are the 3 formulas for acceleration?
Acceleration formula – three acceleration equations
- a = (v_f – v_i) / Δt ;
- a = 2 × (Δd – v_i × Δt) / Δt² ;
- a = F / m ;
Is acceleration the derivative of velocity?
In Physics Acceleration is the derivative of velocity with respect to time: a(t)=ddt(v(t))=d2dt2(x(t)). Momentum (usually denoted p) is mass times velocity, and force (F) is mass times acceleration, so the derivative of momentum is dpdt=ddt(mv)=mdvdt=ma=F.
How do you find acceleration from V vs T graph?
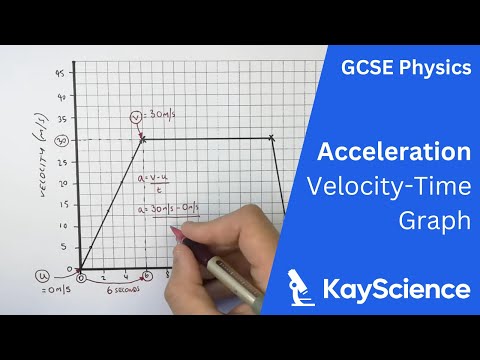
What is velocity calculus formula?
The instantaneous velocity v(t) of a particle is the derivative of the position with respect to time. That is, v(t)=dxdt. This derivative is often written as ˙x(t), or simply as ˙x.
How do you find acceleration vector in calculus?
Is acceleration the second derivative of velocity?
The acceleration of a moving object is the derivative of its velocity – that is, the second derivative of its position function.
How do you find acceleration without final velocity?
Rearrange the equation F = ma to solve for acceleration. You can change this formula around to solve for acceleration by dividing both sides by the mass, so: a = F/m. To find the acceleration, simply divide the force by the mass of the object being accelerated.
What are the 4 equations for acceleration?
Equations of Motion
| Variable | Equation |
|---|---|
| Velocity | v, equals, u, plus, a, t,v=u+at |
| Displacement with positive acceleration | s, equals, u, t, plus, one half, a, t, squared,s=ut+21at2 |
| Displacement knowing initial and final velocities | s, equals, one half, left bracket, u, plus, v, right bracket, t,s=21(u+v)t |
How do you find acceleration with velocity and displacement?
The equation can also be used to calculate the acceleration of an object if its initial and final velocities, and the displacement are known. To do this, rearrange the equation to find a: v 2 − u 2 = 2 a x. a = v 2 − u 2 2 x.
When acceleration is a function of velocity?
Acceleration is the rate of change of an object’s velocity. Just like the derivative of the position function gives you the velocity as a function of time, the derivative of the velocity function (which is also the second derivative of the position function) gives you the acceleration as a function of time.
How do you find velocity function?
How do you find acceleration with VI and VF?
Use the formula to find acceleration. First write down your equation and all of the given variables. The equation is a = Δv / Δt = (vf – vi)/(tf – ti). Subtract the initial velocity from the final velocity, then divide the result by the time interval. The final result is your average acceleration over that time.
