How do you find average acceleration kinematics?
How do you find average acceleration kinematics?
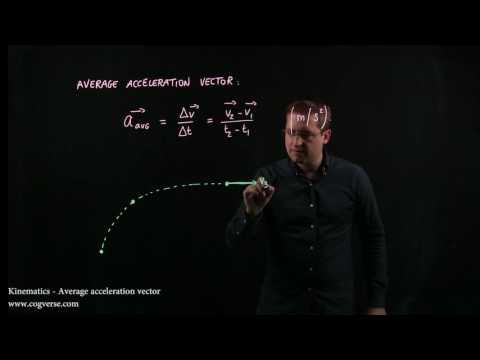
How do you calculate average acceleration with example?
Average Acceleration – Definition The change in velocity divided by the elapsed time is the average acceleration. For example, if a marble’s velocity increases from 0 to 60 cm/s in three seconds, its average acceleration is 20 cm/s. This indicates that every second, the marble’s velocity will rise by 20 cm/s.
What is average acceleration SHM?
The displacement in one cycle in SHM is zero, since particle returns to original position. Hence, average velocity and average acceleration both become zero.
How do you find average acceleration without time?
If you know that acceleration is constant, you can solve for it without time if you have the initial and final velocity of the object as well as the amount of displacement. Use the formula v^2=u^2+2as where v is the final velocity, u is the initial velocity, a is acceleration, and s is displacement.
What’s average acceleration?
Average acceleration, is defined as the rate of change of velocity, or the change in velocity per unit time. The units of acceleration are distance over time squared.
What are the 4 kinematics formulas?
There are four basic kinematics equations: v = v 0 + a t. Δ x = ( v + v 0 2 ) t. Δ x = v 0 t + 1 2 a t 2. v 2 = v o 2 + 2 a Δ x.
Can we find average acceleration?
We divide the change in velocity by an elapsed time to find out the average acceleration of anything.
Is average acceleration the same as constant acceleration?
So if you changed your velocity by an amount Δv in a time Δt, the average acceleration is “that constant acceleration that you would have to have to change your velocity that much in that time”. Of course you might not have moved with a constant acceleration in that time interval.
What is averaging formula?
Average This is the arithmetic mean, and is calculated by adding a group of numbers and then dividing by the count of those numbers. For example, the average of 2, 3, 3, 5, 7, and 10 is 30 divided by 6, which is 5.
What is average velocity and acceleration?
Velocity is the rate of displacement of an object. It is measured in m/s. Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity of an object.
What is the symbol for average acceleration?
Summary. Acceleration is the rate at which velocity changes. In symbols, average acceleration ˉa is ˉa=ΔvΔt=vf−v0tf−t0. The SI unit for acceleration is 2 .
What is average acceleration class 11th?
Average acceleration is the change in velocity divided by an elapsed time. For instance, if the velocity of a marble increases from 0 to 60 cm/s in 3 seconds, its average acceleration would be 20 cm/s2.
How do you find average acceleration with force?
Summary. According to Newton’s second law of motion, the acceleration of an object equals the net force acting on it divided by its mass, or a = F m . This equation for acceleration can be used to calculate the acceleration of an object when its mass and the net force acting on it are known.
How do you find average acceleration from a velocity vs time graph?
How do you find acceleration with average speed and time?
Summary
- To calculate average acceleration when direction is not changing, divide the change in velocity by the change in time using the formula: acceleration = Δ v Δ t.
- The SI unit for acceleration is m/s2.
How do you find average acceleration GCSE?
How do you find average velocity in kinematics?
Because kinematics equations are used when the acceleration of the object is constant, we can use a simple equation to determine the average velocity of an object. To find the average velocity, simply add the initial velocity to the final velocity and divide by 2.
