How do you find tangential acceleration vector?
How do you find tangential acceleration vector?

What is the tangential component of acceleration?
The tangential acceleration is a measure of the rate of change in the magnitude of the velocity vector, i.e. speed, and the normal acceleration are a measure of the rate of change of the direction of the velocity vector.
How do you find the components of an acceleration vector?
2: Tangential and Normal Components of Acceleration. a⇀N=⇀a⋅⇀N=||⇀v×⇀a||||⇀v||=√||⇀a||2−(a⇀T)2. ⇀a(t)=a⇀T⇀T(t)+a⇀N⇀N(t). Here ⇀T(t) is the unit tangent vector to the curve defined by ⇀r(t), and ⇀N(t) is the unit normal vector to the curve defined by ⇀r(t).
How do you find acceleration on a calculator?
How do you calculate acceleration? Acceleration (a) is the change in velocity (Δv) over the change in time (Δt). It can be calculated using the equation a = Δv/Δt.
How do you find the tangential acceleration example?

How do you find tangential acceleration and centripetal acceleration?
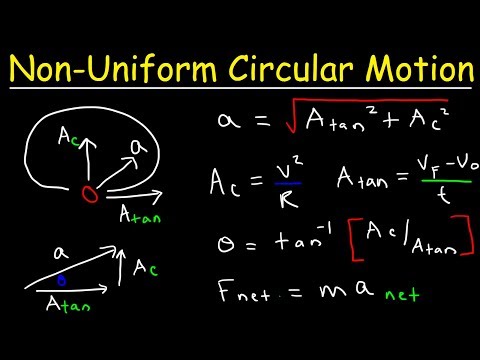
What is tangential component of a vector?
In mathematics, given a vector at a point on a curve, that vector can be decomposed uniquely as a sum of two vectors, one tangent to the curve, called the tangential component of the vector, and another one perpendicular to the curve, called the normal component of the vector.
Is tangential acceleration always zero?
So, during a uniform circular motion tangential acceleration is zero due to its constant angular velocity. Note: It must be noted that during a uniform circular motion, the tangential acceleration is zero as the angular velocity is constant.
Is tangential acceleration the same as total acceleration?
The tangential acceleration is tangential to the circle at the particle’s position. The total acceleration is the vector sum of the tangential and centripetal accelerations, which are perpendicular.
How do you find the tangential and radial components of acceleration?
The tangential component causes a change in speed and its magnitude is given by at = dv/dt, and the radial component causes a change in direction and its magnitude is given by ar = v2/r, where r is the radius of curvature at the point in question.
How do you calculate tangential and normal acceleration?
What are the 3 formulas for acceleration?
Acceleration formula – three acceleration equations
- a = (v_f – v_i) / Δt ;
- a = 2 × (Δd – v_i × Δt) / Δt² ;
- a = F / m ;
What are the 4 equations for acceleration?
Equations of Motion
| Variable | Equation |
|---|---|
| Velocity | v, equals, u, plus, a, t,v=u+at |
| Displacement with positive acceleration | s, equals, u, t, plus, one half, a, t, squared,s=ut+21at2 |
| Displacement knowing initial and final velocities | s, equals, one half, left bracket, u, plus, v, right bracket, t,s=21(u+v)t |
How do you calculate acceleration example?
How many formulas are there for acceleration?
There are five frequently used formulas for motion in a straight line with constant acceleration. The formulas are given in terms of the initial velocity u, the final velocity v, the displacement (position) x, the acceleration a and the time elapsed t. Of course, they require consistent systems of units to be used.
How do you find the unit tangent vector?
How do you show a vector is tangential to a surface?
Directional derivatives are one way to find a tangent vector to a surface. A tangent vector to a surface has a slope (rise in z over run in xy) equal to the directional derivative of the surface height z(x,y).
What is the formula for tangential force?
Σ F = m a the equation shows how an unbalanced force must be acting to cause negative acceleration or deceleration. The force produced is called a tangential force.
How do you find tangential and radial acceleration?
Radial acceleration equals tangential velocity squared divided by the radius so that the tangential velocity squared equals the radial acceleration times the radius. Taking the square root of both sides of the equation results with the tangential velocity equaling 22.4 m/s.
