How do you find the unit tangent vector?
How do you find the unit tangent vector?

What is a unit tangent vector?
The Unit Tangent Vector The derivative of a vector valued function gives a new vector valued function that is tangent to the defined curve. The analogue to the slope of the tangent line is the direction of the tangent line.
How do you find the unit tangent vector in Calc 3?

What is a unit vector calculator?
This unit vector calculator will help you transform any vector into a vector of length 1 without changing its direction. If you want to know how to calculate a unit vector’s components, look no further! You can obtain the result by dividing the components of any arbitrary vector by its magnitude.
How do you find unit tangent and unit normal vectors?
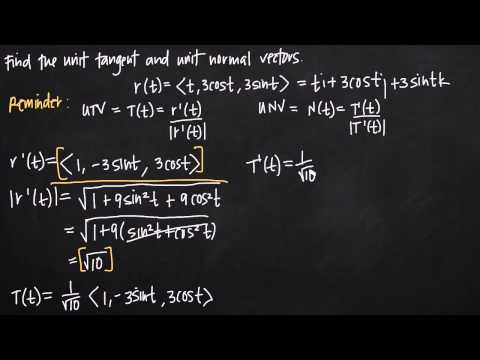
How do you find the tangent vector of a curve at a point?
You need to figure out which value of t corresponds to the point (0,0,1), that is, which number t solves the equation r(t)=(0,0,1)? Then take the derivative of r with respect to t, and plug in the value that you found above. The result will be a tangent vector for the curve at the point (0,0,1).
What is unit vector function?
These unit vectors are commonly used to indicate direction, with a scalar coefficient providing the magnitude. A vector decomposition can then be written as a sum of unit vectors and scalar coefficients.
What is the formula for unit normal vector?
Unit Normal Vector Any nonzero vector can be divided by its length to form a unit vector. Thus for a plane (or a line), a normal vector can be divided by its length to get a unit normal vector. Example: For the equation, x + 2y + 2z = 9, the vector A = (1, 2, 2) is a normal vector. |A| = square root of (1+4+4) = 3.
What is unit vector unit and dimension?
A unit vector has no dimension.
II, A unit vector has unit magnitude.
What is a unit vector in Calc 3?
A unit vector is a vector whose length is 1.
What is a unit vector in 3 dimensions?
The standard unit vectors in three dimensions. The standard unit vectors in three dimensions, i (green), j (blue), and k (red) are length one vectors that point parallel to the x-axis, y-axis, and z-axis respectively.
How do you find the tangent line in Calculus 3?
What is unit vector and equal vector?
Solution : A vectors whose magnitude is unity, is known as a unit vectors. If the magnitude and direction of two vectors are same, then the two vectors are called equal vectors.
How many unit vectors are there?
There is only one unit vector in a given direction. There is only one value for the expression v / |v|. There is only one unit vector in the positive x direction, represented by ( +1, 0)T. The same is true for other orientations and other number of dimensions.
What is the unit vector of an angle?
You do not find the unit vector of an angle, but instead you find the unit vector from any vector that has a different length. A vector has two principle properties, its angle and its magnitude. You can determine the magnitude from the X and Y components of that vectors movement.
Is a tangent space a vector space?
The tangent space of a differentiable manifold M is a vector space at a point p on the manifold whose elements are the tangent vectors (or velocities) to the curves passing through that point p. The tangent space at this point p is usually denoted TpM.
What is vector equation for the tangent line?
A parametrization of the line through a point a and parallel to the vector v is l(t)=a+tv. Setting a=c(t0) and v=c′(t0), we obtain a parametrization of the tangent line: l(t)=c(t0)+tc′(t0).
