How is e MC2 so simple?
How is e MC2 so simple?
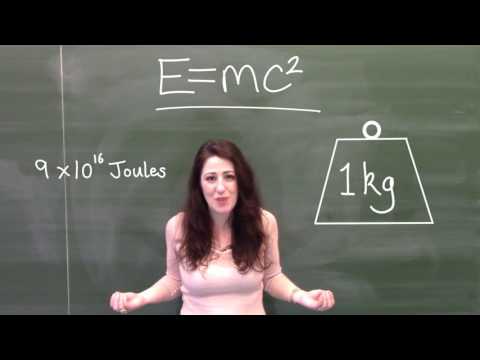
Is E MC2 a theory or fact?
Einstein Was Right (Again): Experiments Confirm that E= mc2 | NIST.
Why is E MC2 so important?
Einstein’s greatest equation, E = mc2, is a triumph of the power and simplicity of fundamental physics. Matter has an inherent amount of energy to it, mass can be converted (under the right conditions) to pure energy, and energy can be used to create massive objects that did not exist previously.
Why did Einstein square the speed of light?
But why is the speed of light squared? The reason is that kinetic energy, or the energy of motion, is proportional to mass. When you accelerate an object, the kinetic energy increases to the tune of the speed squared.
How is E mc2 used in everyday life?
When you drive your car, E = mc2 is at work. As the engine burns gasoline to produce energy in the form of motion, it does so by converting some of the gasoline’s mass into energy, in accord with Einstein’s formula. When you use your MP3 player, E = mc2 is at work.
What problem does E mc2 solve?
The E = mc2 calculator can solve for E or m. If you know the mass of an object, m, you can solve for E, its intrinsic energy. Or if you have an amount of energy you can solve for m, its equivalent mass.
Is E mc2 practically proven?
It’s taken more than a century, but Einstein’s celebrated formula e=mc2 has finally been corroborated, thanks to a heroic computational effort by French, German and Hungarian physicists.
What is the proof for Einstein’s theory of relativity?
Tests of general relativity General relativity has also been confirmed many times, the classic experiments being the perihelion precession of Mercury’s orbit, the deflection of light by the Sun, and the gravitational redshift of light. Other tests confirmed the equivalence principle and frame dragging.
Is it possible to travel faster than the speed of light?
Within conventional physics, in accordance with Albert Einstein’s theories of relativity, there’s no real way to reach or exceed the speed of light, which is something we’d need for any journey measured in light-years. That hasn’t stopped physicists from trying to break this universal speed limit, though.
What is the purpose of Einstein’s theory of relativity?
Formulated by Albert Einstein beginning in 1905, the theory of relativity explains the behavior of objects in space and time, and it can be used to predict things such as the existence of black holes, light bending due to gravity and the behavior of planets in their orbits.
What is the purpose of the theory of relativity?
The theory explains the behaviour of objects in space and time, and it can be used to predict everything from the existence of black holes, to light bending due to gravity and the behaviour of the planet Mercury in its orbit. Einstein’s relativity theory is deceptively simple and consists of just three rules.
Why speed of light is impossible?
Nothing can travel faster than 300,000 kilometers per second (186,000 miles per second). Only massless particles, including photons, which make up light, can travel at that speed. It’s impossible to accelerate any material object up to the speed of light because it would take an infinite amount of energy to do so.
Why can nothing go faster than the speed of light?
According to the laws of physics, as we approach light speed, we have to provide more and more energy to make an object move. In order to reach the speed of light, you’d need an infinite amount of energy, and that’s impossible!
What are the 3 laws of Einstein?
I begin the discussion by offering the following three laws: ▸ The laws of physics are identical in all non-accelerating (that is, inertial) frames. ▸ The vacuum speed of light, c, is the same for all inertial frames. ▸ The total energy E of a body of mass m and momentum p is given by E=√m2c4+p2c2.
Is energy created or destroyed?
The law of conservation of energy states that energy can neither be created nor destroyed – only converted from one form of energy to another. This means that a system always has the same amount of energy, unless it’s added from the outside.
What is an example of Einstein’s theory of relativity?
One example of relativity is to imagine two people on a train playing ping-pong. The train is traveling at around 30 m/s north. When the ball is hit back and forth between the two players, the ball appears to the players to move north at a speed of around 2 m/s and then south at the speed of 2 m/s.
What did Einstein say about energy?
Einstein said, “Everything is energy and that’s all there is to it. Match the frequency of the reality you want and you cannot help but get that reality.
Is the theory of relativity still a theory?
This theory is still considered to be the most important idea in modern physics. It rewrote Isaac Newton’s physical laws devised 200 years earlier and created an elegant way to understand the Universe.
Can a fact be a theory?
A theory never becomes a fact. It is an explanation of one or more facts. A well-supported evidence-based theory becomes acceptable until disproved. It never evolves to a fact, and that’s a fact.
Is Einstein’s theory?
Einstein’s 1915 general theory of relativity holds that what we perceive as the force of gravity arises from the curvature of space and time. The scientist proposed that objects such as the sun and the Earth change this geometry.
Is relativity a theory?
Albert Einstein’s theory of relativity is actually two separate theories: his special theory of relativity , postulated in the 1905 paper, The Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies and his theory of general relativity , an expansion of the earlier theory, published as The Foundation of the General Theory of Relativity in …
