What is the kinetic energy formula with an example?
What is the kinetic energy formula with an example?
In classical mechanics, kinetic energy (KE) is equal to half of an object’s mass (1/2*m) multiplied by the velocity squared. For example, if a an object with a mass of 10 kg (m = 10 kg) is moving at a velocity of 5 meters per second (v = 5 m/s), the kinetic energy is equal to 125 Joules, or (1/2 * 10 kg) * 5 m/s2.
What are the two formulas for kinetic energy?
Difference Between Kinetic Energy and Potential Energy
| Kinetic energy | Potential energy |
|---|---|
| Formula used is K E = 1 2 m v 2 | The formula used is mgh |
| Vibrational energy is an example of kinetic energy | Gravitational potential energy is an example of potential energy |
How do you calculate kinetic energy GCSE?
Ek = ½ × m × v2 Ek = kinetic energy in Joules (J) m = mass of the object in kilograms (kg) v = speed of the object in metres per second (m/s)
How do you solve a KE?
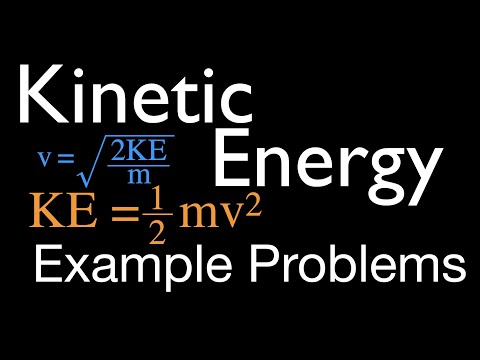
How do you find final kinetic energy?
Final kinetic energy KE = 1/2 m1v’12 + 1/2 m2v’22 = joules. For ordinary objects, the final kinetic energy will be less than the initial value. The only way you can get an increase in kinetic energy is if there is some kind of energy release triggered by the impact.
What is kinetic equation in physics?
The kinematic equations are a set of equations that describe the motion of an object with constant acceleration. Kinematics equations require knowledge of derivatives, rate of change, and integrals.
What is unit kinetic energy?
The units of kinetic energy are mass times the square of speed, or kg · m 2 /s 2 kg · m 2 /s 2 . But the units of force are mass times acceleration, kg · m/s 2 kg · m/s 2 , so the units of kinetic energy are also the units of force times distance, which are the units of work, or joules.
What is kinetic energy expression?
The energy by virtue of motion is called as kinetic energy. An object that has motion, whether it may be vertical or horizontal motion, has kinetic energy. Kinetic energy depends on mass(m) of the object and speed (v) of the object. The equation used to represent kinetic energy is: KE=12mv2.
What are the 3 types of kinetic energy?
What Are the Types of Kinetic Energy?
- Translational.
- Rotational.
- Vibrational kinetic energy.
What is kinetic energy GCSE physics?
Kinetic energy is the energy an object possesses by virtue of its movement. The amount of kinetic energy possessed by a moving object depends on the mass of the object and its speed . The greater the mass and the speed of the object the greater its kinetic energy.
What is the KE energy formula?
Kinetic energy is directly proportional to the mass of the object and to the square of its velocity: K.E. = 1/2 m v2. If the mass has units of kilograms and the velocity of meters per second, the kinetic energy has units of kilograms-meters squared per second squared.
What is the value for KE?
The Coulomb constant, the electric force constant, or the electrostatic constant (denoted ke, k or K) is a proportionality constant in electrostatics equations. In SI base units it is equal to 8.9875517923(14)×109 kg⋅m3⋅s−4⋅A−2.
What is energy formula?
The equation developed by Albert Einstein, which is usually given as E = mc2, showing that, when the energy of a body changes by an amount E (no matter what form the energy takes), the mass (m) of the body will change by an amount equal to E/c2.
What is kinetic energy and examples?
Kinetic energy is the energy of motion, observable as the movement of an object, particle, or set of particles. Any object in motion is using kinetic energy: a person walking, a thrown baseball, a crumb falling from a table, and a charged particle in an electric field are all examples of kinetic energy at work.
What are 5 examples of kinetic?
By keeping this formula in mind, let us take a few examples where we observe kinetic energy in our day-to-day life.
- Hydropower Plants. ADVERTISEMENT. …
- Wind Mills. Windmills form one of the good examples of applications of kinetic energy. …
- Moving Car. …
- Bullet From a Gun. …
- Flying Airplane. …
- Walking & Running. …
- Cycling. …
- Rollercoasters.
Which is the best example of kinetic energy?
Anything at home that moves is an example of kinetic energy. This could be a cue ball rolling on a billiards table, a fan circulating air on a warm day, or glass shattering on the floor after it falls from the counter. Electrical devices that are turned on use kinetic energy as do people moving about the house.
What is kinetic energy formula Class 9?
The expression for kinetic energy is given as- 12mv2 where ‘m’ is mass of the body and ‘v’ is the speed of the object. It is produced by the movement of the body.
