How to calculate the acceleration due to gravity on the moon?
How to calculate the acceleration due to gravity on the moon?
- Divide the mass of the Moon (7.346 x 10²² kg) by the square of its radius (1737.4 km).
- Multiply the result from step 1 with 6.674×10⁻¹¹ m³/kg s², i.e., the value of G.
- Congrats!
- Divide the mass of the Moon (7.346 x 10²² kg) by the square of its radius (1737.4 km).
- Multiply the result from step 1 with 6.674×10⁻¹¹ m³/kg s², i.e., the value of G.
- Congrats!
How do you find acceleration due to gravity with mass and radius?
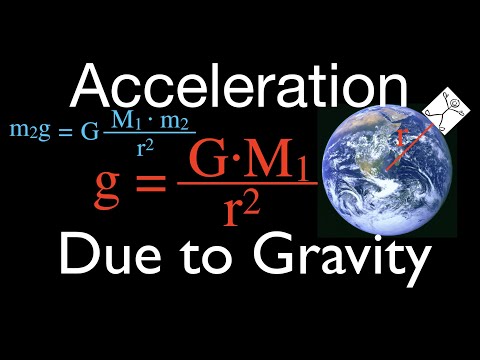
Formula for Acceleration Due to Gravity These two laws lead to the most useful form of the formula for calculating acceleration due to gravity: g = G*M/R^2, where g is the acceleration due to gravity, G is the universal gravitational constant, M is mass, and R is distance.
What is the acceleration due to gravity of the moon Class 10?
The acceleration due to gravity on moon or the value of g on moon is 1.625 m/s2.
What is the acceleration due to gravity on the surface of the moon Use 7.35 1022 kg and 1740 km for the mass and the radius of the moon?
The acceleration due to gravity on the surface of the moon is 1. 620 ms2.
What is the formula of acceleration due to gravity?
Its value near the surface of the earth is 9.8 ms-2. Therefore, the acceleration due to gravity (g) is given by = GM/r2.
How do you calculate acceleration due to gravity example?
What is acceleration due to gravity in physics class 9?
When an object falls freely towards the surface of earth from a certain height, then its velocity changes and this change in velocity produces acceleration in the object which is known as acceleration due to gravity denoted by g. The value of acceleration due to gravity is. g=9. 8m/s2.
How to calculate acceleration?
Acceleration (a) is the change in velocity (Δv) over the change in time (Δt), represented by the equation a = Δv/Δt. This allows you to measure how fast velocity changes in meters per second squared (m/s^2).
How do you find the value of g Class 9?
- G is the universal gravitational constant, G = 6.674×10–11m3kg–1s–2.
- M is the mass of the massive body measured using kg.
- R is the radius of the massive body measured using m.
- g is the acceleration due to gravity measured using m/s2.
- G is the universal gravitational constant, G = 6.674×10–11m3kg–1s–2.
- M is the mass of the massive body measured using kg.
- R is the radius of the massive body measured using m.
- g is the acceleration due to gravity measured using m/s2.
What is the value of gravitational constant g on the moon Class 9?
The acceleration due to gravity on the surface of the Moon is about 1.625 m/s2, about 16.6% that on Earth’s surface or 0.16 ɡ. [1]Over the entire surface, the variation in gravitational acceleration is about 0.0253 m/s2 (1.6% of the acceleration due to gravity).
What is the direction of acceleration due to gravity explain with an example class 9?
The acceleration due to gravity of Earth always acts in downward direction.
What is acceleration class 10th?
Acceleration is defined as. The rate of change of velocity with respect to time. Acceleration is a vector quantity as it has both magnitude and direction. It is also the second derivative of position with respect to time or it is the first derivative of velocity with respect to time.
What is the value of acceleration due to gravity at 6.4 * 10 6 m altitude?
The value of acceleration due to gravity at Earth’s surface is 9.8 ms−2. The altitude above its surface at which the acceleration due to gravity decreases to 4.9 ms−2, is close to (Radius of earth =6.4×106 m ) No worries!
What does it mean acceleration due to gravity of moon is 1.67 m per second square?
Acceleration on moon is 1.67 m/s². This means that when an object is dropped from a height on the moon, its velocity increases by 1.67 m/s every second. Also, with respect to Earth’s gravity (g = 9.8 m/s²), the gravity of moon is less than that of earth.
Is the acceleration due to gravity on moon is 1/6 that of the earth?
The acceleration due to gravity on the surface of the Moon is approximately 1.625 m/s2, about 16.6% that on Earth’s surface or 0.166 ɡ. Over the entire surface, the variation in gravitational acceleration is about 0.0253 m/s2 (1.6% of the acceleration due to gravity).
What is the acceleration due to gravity g on the moon if g is 10ms 2 on the earth?
Explanation: The acceleration due to gravity of the moon is 1.67m/s2.
How do you calculate free fall acceleration on the moon?
- T=2π√lg.
- l=1.7m.
- The acceleration due to gravity on earth is g=9.8ms−2.
- T=2π√1.709.8.
- On the moon, the acceleration due to gravity is g1=1.62ms−2.
- 2π√l1g1=2π√1.79.8.
- l1=1.79.8⋅1.62=0.281m.
- T=2π√lg.
- l=1.7m.
- The acceleration due to gravity on earth is g=9.8ms−2.
- T=2π√1.709.8.
- On the moon, the acceleration due to gravity is g1=1.62ms−2.
- 2π√l1g1=2π√1.79.8.
- l1=1.79.8⋅1.62=0.281m.
How do you calculate the acceleration of the moon towards the earth’s center?
M=5.972×1024kg is the mass of the Earth and m is the mass of the moon. Plugging in the values, we get: →ar=6.674×10−11×5.972×1024(3.844×108)2=2.7×10−11+24−16, which is consistent with our result.
How to find the acceleration due to gravity on another planet?
Steps for Calculating the Acceleration Due to Gravity on a Different Planet. Step 1: Identify the mass and radius of the planet. Step 2: Calculate the acceleration due to gravity on the surface of that planet using the equation g=GMR2 g = G M R 2 .
